Periodontal disease in dogs
The perils of gum disease in dogs
the Silent Killer
What is periodontal disease? |
Gingivitis - the first stage |
How does untreated gingivitis progress to periodontal disease in dogs? |
Characteristics signs of periodontal disease in dogs |
Photos and descriptions of the 4 stages of periodontal disease in dogs
Periodontal disease treatment in dogs |
Top 10 dog breeds prone to progressive periodontal disease
What is periodontal disease?
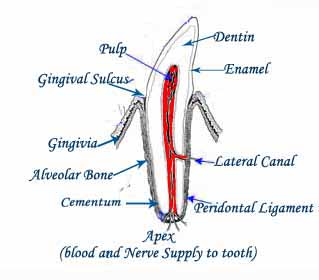
The word periodontal comes from two Greek words that mean "around the tooth". Periodontal disease in dogs occurs in two forms - gingivitis and periodontitis
Gingivitis
If caught early and treated correctly the condition is generally reversible.
Periodontitis develops as a progression of untreated gingivitis, whereby gingivitis has advanced to the point whereby the deeper structures supporting the dog's teeth have become inflamed and or pussy.
Periodontal disease in dogs is one of the most common causes of infectious diseases in the world of dogs, and is the leading cause of both tooth and bone loss. Once teeth and bone loss has occurred the condition is irreversible.
In human dentistry, periodontal disease is called the "silent killer" due to its insidious and destructive nature. The same name can be aptly applied in the world of animals.
How does untreated gingivitis progress to periodontal disease in dogs?

The tissue covering the outside of the roots of teeth is called "cementum". Cementum along with the surrounding connective tissues of the periodontal membranes, hold and support teeth in their sockets. This works perfectly, until infection and inflammation of the early stages of gingivitis become part of the equation
Gum Infections attack the periodontal membranes, and over time if not treated the infection becomes worse and worse. Eventually the dog's teeth become involved and infected by the entry of bacteria through the apexes of their roots.
At this stage, teeth begin to loosen and or abscess and eventually they detach and fall out. This is an horrendously painful process for your dog and should never be allowed to happen.
Once infection has progressed to the point of periodontal disease, bacteria can enter the bloodstream and cause the spread of other oral related bacterial infections to Other Organs of the Dog's Body, including brain, heart, kidney, lungs and liver.
Characteristics signs of periodontal disease in dogs

- Severe halitosis or foul smelling breath
- Severe and constant throbbing pain
- Dribbling, drooling and whimpering while eating
- Difficulty or reluctance to eat
- A thick build up of yellowy-brown calculus covering the teeth surfaces
- Red and inflamed gums, especially at the teeth/gum margins
- Bleeding and suppurating (pus filled) gums
- Loose teeth or loss of teeth
- Ruptured abscesses which can cause maxillary (upper jaw) sinus or nasal cavity pus discharges
- Depression
- Mandibular (lower jaw) fractures in the most advanced cases
Photos and descriptions of the 4 stages of periodontal disease in dogs
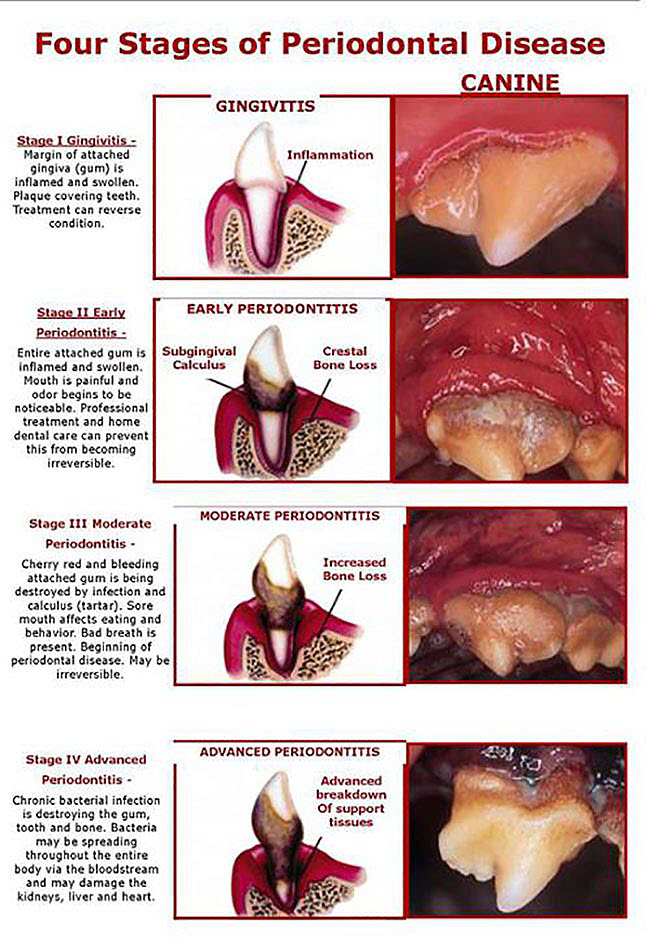
Four stages of canine Periodontal Disease
Photos and descriptions with courtesy of Prairie View Animal Hospital
Periodontal disease treatment in dogs
Your dog's teeth should be Cleaned By Your Vet, together with a course of antibiotics. Depending on the severity of the gum disease present, teeth may need to be extracted and or a gingivectomy procedure done.

As already stated above, periodontal disease in dogs is rarely reversible. To try and maintain the degree of dental health that your vet established by cleaning your dog's teeth it is essential that you do your very best to introduce:
- regular 6-12 monthly dental checks with your vet
- an home oral care plan, including cleaning Fido's teeth at least once or twice a day
- soft raw bones such as soft brisket bones or chicken necks
- chew bars or toys like Pigs Ears and Lamb Ears pictured to your right into his diet. Make sure the chews are made locally and not imports from Asia, commonly referred to as Rawhide. Please read our article on Rawhide and make yourself aware of the shocking chemical process used by China and Thailand to make them.
Top 10 dog breeds prone to progressive periodontal disease
Keeping your dog's gums and teeth in tip top shape takes time, patience and money. Here's a list of breeds to avoid if you are short on any of these factors:
- Bichon Frise
- Chihuahua
- Chinese Crested - Hairless
- Greyhound
- Italian Greyhound
- Maltese
- Pomeranian
- Toy and Miniature Poodles
- Shih Tzu
- Sitehounds (most breeds)
- Yorkshire Terrier

This article and information forms part of the Carole's Doggie World Holistic Library and is presented for informational purposes only.The information is not intended to be a substitute for visits to your local vet. Instead, the content offers the reader information researched and written by Carole Curtis for www.carolesdoggieworld.com







